 Call at :
+86 18681515767
Call at :
+86 18681515767
 Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
 Call at :
+86 18681515767
Call at :
+86 18681515767
 Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
01. Our Products
Hot ProductsShenzhen Jietong Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech company focusing on the development, production and sales of radio frequency identification (RFID).
ALWAYS ONE STEP MORE!
COMPANY PROFILE Shenzhen Jietong Technology Co., Ltd. (brand JTSPEEDWORK)was established in 2011 and is anational high-tech enterprise integrating R&D, manufacturing, sales and service. We focuses on the research and development of RFlD readers and modules, mainly covering LF, HF,UHF, and 2.4G, and we are the first company to cover the full range of RFlD technology. Independent core research and development of products, supporting customized needs, unified RFlD readerprotocol, quick response RFlD hardware platform, one-stop rfid hardware solution provider. JTSPEEDWORK has been committed to providing customers with high-performance RFlD reader andwriter products. The core R&D personnel of the technical team have more than 10 years of experience in the RFlD industry. Related products have obtained SRRC,CE,FCC,ROHS,C-TICK,TELEC certification. Products are widely used in garbage sanitation classification, shared electric vehicles, intelligentmanufacturing,warehousing,asset management, personnel management, intelligent animahusbandry, clothing management, smart transportation, electricity and other intelligent data identification and collection fields. 10000+ From its establishment in 2011 to 2023, the company has achieved a stable performance growth rate of more than 50%, At the end of 2022, annual product sales will break a record high. 128+ With the development of the RFlD market,our business covers china, Southeast Asia,Europe, North America and other regions. 36+ Since its establishment, the company has been increasing investment and insisting on foreign trade. Currently, our RFlD reading and writing equipment has been exported to 36 countries and regions around the world. WISH MISSION VALUE 2011 Built 20+Engineers 1500㎡Area The leader of RFlD industry Make data collection and control easier Focus, innovation, hard-work, wir-win

02. WHY CHOOSE US
OUR ADVANTAGEShenzhen Jietong technology Co. Ltd., is a high-tech company focused on R&D, production and sales of radio frequency identification (RFID ). Special professional in UHF RFID series reader of internet of things. Jietong has own R&D team which the engineers has more than 10 years of R&D experience. In order to provide the best service and product to customer, Jietong is in continuously development to offer whole solution for the project, after-sale service and technology support. Jietong has main product lines which include UHF RFID module, RFID Handheld Reader, UHF RFID Reader, Car parking middle range RFID Reader , UHF access control reader, UHF antenna, UHF cards and Tag, etc., JT UHF RFID Reader already used in vehicle management intensively, using environment also include staff management for factory, weight management for warehouse, access control for warehouse and vehicle, clothing management, the tobacco logistics management, intelligent library management, production line identification management, asset management etc., Jietong has the principle of the supremacy of users, and depends on market-oriented, new technology and high quality, we will provide the latest technology, the best products, the competitive, the sincerely service to our clients.
 Professional
Professional
The R&D team has more than 10 years of experience;
 Products
Products
Offer low cost, middle and high quality product;
 Quality
Quality
National patent protection for own brand product
 Service
Service
2 years warranty and 3 years cost-maintenance;
03. PROJECT CASES
SOLUTION&CASEThis solution page helps customers solve the problem of installing and managing applications using Jietong Technology's products. The following are included: Vehicle management UHF personal system management Production line management Logistics management Asset management Warehouse management Environmental sanitation vehicles manage Intelligent bookcase management
RFID Technology in the Renewable Energy Sector: Applications and Opportunities 1. Introduction As the global renewable energy industry expands, efficient asset management, supply c...
Read More
RFID Technology in Smart Parking Systems 1. Technical Principles RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) parking systems utilize wireless radio frequency identification to enable non...
Read More
UHF RFID Personnel management system >> System Overview Long-distance card staff management system is the modern personnel management system with the combination of the UHF R...
Read More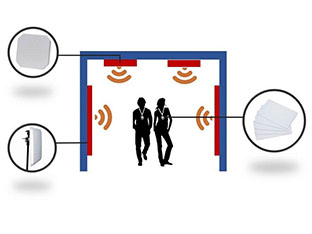
Production line management In order to produce better quality products, while reducing production costs and meeting the requirements of ISO 9000, manufacturers are more closely tra...
Read More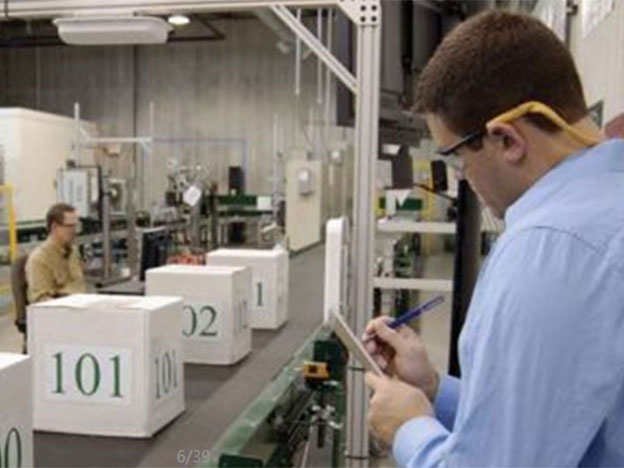
AGV Trolley Track Guidance Management With the manufacturing level and increasing customer demand, a variety of logistics systems are facing many challenges, such as how to improve...
Read More
Asset RFID Management System System overview The way to manually implement the asset management including the asset increase, distribution, storage, disposal, etc. can never satisf...
Read More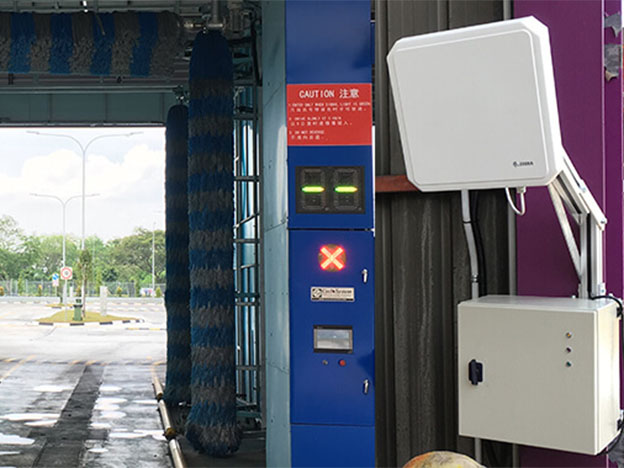
04. EVENTS
latest newsInformation related to the actual application cases of RFID technology is collected here, and each project is our valuable experience and valuable for reference.


05. FREE CONSULTATION
Leave A MessageIf you are interested in our products and want to know more details,please leave a message here,we will reply you as soon as we can.

Phone : +86 18681515767
Whatsapp : +8618681515767

Email : marketing@jtspeedwork.com

4/F,7 Building,Lihe industry, NO.1055 Songbai Road ,Nanshan District, Shenzhen, China
Copyright © 2025 Shenzhen Jietong Technology Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

IPv6 network supported